Insulin - Things You Should Know
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to control the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood. In people who have diabetes, the pancreas does not produce any or enough insulin, or body is unable to effectively use the insulin it does produce. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream.
Insulin and type 1 diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes do not naturally produce any insulin. As a result, they need to take insulin every day.
Insulin and type 2 diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes, you may be able to keep your blood glucose levels in your target range through healthy eating, physical activity and by taking diabetes medication. Ask your doctor to refer you to a registered dietitian to learn about healthy eating. You should follow PG Medical Guidelines for Healthy Eating, which includes limiting the amount of carbohydrates and fats you eat. THERE IS NO SUCH THING AS SPECIAL DIABETIC DIET!
(Contact Dr. Lalwani's Clinic for diet counseling)
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition and over the years most people (in fact all-if they survice long enough !) with type 2 diabetes will need to use insulin to properly manage blood glucose. If your body is not producing enough despite drugs being taken then you will have to take Insulin from "Outside"a! as simple as that!
The most important thing is to manage your diabetes and prevent complications. If you’re nervous about learning to inject insulin, take heart – even young children can master this skill with practice. As well, modern injection devices, such as insulin pens, are virtually painless.
Types of insulin-Available Now…..
When insulin was first made available for people with diabetes, there was only one kind: short-acting insulin, which required several injections a day. Today, many different types of insulins are available, offering more flexibility in the number and timing of injections you may need and making it easier for you to maintain your target blood glucose levels.
A)Conventional Insulins:Regular, NPH, Premixed 30/70 & now best of the Insulins as:
B)Rapid- and Long-Acting Insulin Analogues
New rapid-acting insulin analogues have been designed to mimic the normal physiologic insulin response that occurs in nondiabetics. Three insulin analogues, insulin Lispro ,Glulisine and Aspart, show improved glycemic control over human insulin in both type 1 and type 2 disease.
In particular, analogues improve postprandial blood(PP) glucose control with a lower risk of Hypoglycemia. Analogs work rapidly after injection, within 5-15 minutes, peak at 60-90 minutes, and last in body for about 4 hours. Human regular insulin(older ones), by contrast, begins to act 30 minutes after injection, peaks at 2-4 hours, and lasts 6-8 hours or longer.
Now a days still longer acting analogs are being talked about like "Degludec Insulin".Idea is to have once or twice a week injections of a Basal Insulin!This will reach us soon! Degludec when used daily can be injected at anytime of the day unrelated to meals and still gives a good control!
Evidence from clinical studies indicates that more aggressive early treatment is clearly a way to reduce the many complications associated with diabetes and to improve the quality of life of people with this disease.
You may need one to four injections a day for optimal management of your blood glucose.
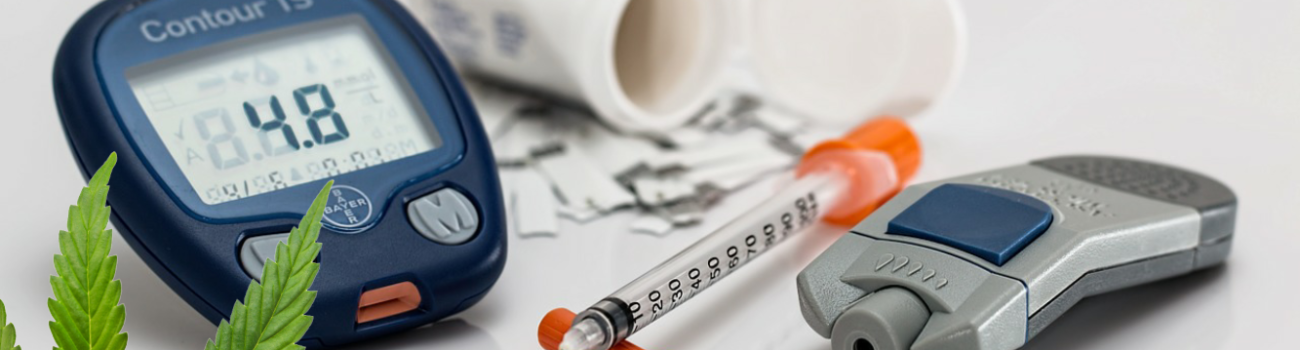
If you take insulin, you need to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly. Regular monitoring is the best way to keep your blood glucose levels in their target range. Regular checks also give you important information about how your blood glucose levels vary during the day, how much insulin you need and if you’re on track in managing your diabetes.
When prescribing an insulin regimen, your doctor will consider several factors, including your treatment goals, age, lifestyle, meal plan, general health, risk of low blood glucose (Hypoglycemia & need for monitoring and testing sugars is always considered), and your financial circumstances. There is no 'one size fits all' plan.
At PG Medical Center Your healthcare team will talk with you about the best insulin plan to meet your needs. Remember, it will take time to fine-tune your insulin regimen, which may change over time depending on life events (such as a major illness) and changes in your lifestyle (such as a new exercise plan).
Talk to your doctor or diabetes educator if you have any questions or concerns about your insulin regimen, or if you aren’t sure how to handle certain situations, such as adjusting your insulin when travelling.
Most Popular and convenient Insulin Delivery system: Insulin Pen
An insulin pen (or just "pen") is an insulin delivery system thatgenerally looks like a large pen, uses an insulin cartridge rather than a vial, and uses disposable needles.
Pens are the predominant insulin delivery system in most of the world. Pens in India are avaibable from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Wockhardt and Aventis.
Some pens use replaceable insulin cartridges, and some pens use a non-replaceable cartridge and are disposed of after use. All pens use replaceable needles. Most pens use special pen needles (see discussion below), which can be extremely short and thin.
Pens With Replaceable Cartridges
Pens with replaceable cartridges are made by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Wockhardt and Aventis.
Insulin cartridges for pens come in 3.0 ml sizes. These 3.0 ml contain 300 units of Insulin. Different Insulins & different combinations are available from all the four manufacturers.
Prefilled Pens
Pens that come with a prefilled insulin cartridge are thrown away when the insulin is used up. Prefilled pens are sold by insulin makers Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Aventis. Lilly only sells prefilled pens which come with a variety of Lilly insulins, including Humalog, Regular, NPH, and various mixes, including Humalog mixes. Novo Nordisk sells both prefilled pens and pens that take replaceable insulin cartridges with Novomix and other Novo Nordisk insulins. Novo Aspart is available as Novo Rapid. Aventis sells prefilled pens with Lantus. Lantus is available as vials, prefilled pens & replaceable cartridges.Levemir is Insulin Detemir from Novo. Apidra is rapid analog from Aventis
Prefilled pens using pre-mixed insulin are usually marketed for use by people with type 2 diabetes. The fixed ratio of insulins does not provide the flexibility needed to accommodate varying food and exercise.
Oral Insulin * Every one is waiting!
Oral insulin is at the very advanced development stage
Oral insulin is a reality: it is simply a matter of when. Insulin injections are extremely harrowing for many diabetics.
Alternative insulin delivery methods
Many alternative delivery systems, although they work to some extent, leave the insulin broken down by digestive juices, usually too much for it to be of significant use to the body.
Insulin like any protein will get digested in stomach.Only if it is made undigestible,it can be absorbed into the blood stream!
Through Nose, mouth and lungs
Nasal delivery issues
Nasal delivery into the upper airway presents severe problems, primarily that the transport system is too convoluted and ineffective.Would require massive, expensive quantities of insulin to reach the target area.
Insulin delivery via lungs
Insulin into the lungs is a promising area: the insulin can be directly absorbed into the bloodstream through the thin walls of the lung. “Insulin Technosphere” holds promise!
Scientists are trying hard to develop methods through which they can make Insulin reach your Blood, bypassing your Digestive system !